The Future of Internet: Web3, Explained
Starting in late 2021 after another record-breaking bitcoin bull run and a show-stopping display of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in New York City’s Times Square, everyday consumers outside the crypto industry began waking up to the potential of blockchain and smart contracts. And thanks to high-profile events like metaverse fashion week, which attracted big-name brands like Dolce and Gabbana, Estée Lauder, and Gucci, the general public is starting to catch whiffs of what blockchain could mean to the future of online experiences.
Unlike web2 — the paradigm we’re currently operating in — web3 promises newfound data sovereignty via blockchain. Through blockchain’s open-source, transparent ledger, it’s theoretically possible for all consumer interactions to be logged and tracked. If things work out, consumers will have the ability to own our own information for once. And if things don’t work out — well, let’s just say that most blockchain developers have no plans to let that happen.
Data sovereignty just scratches the surface of what web3 may offer. The other big benefits of web3 may one day include the ability to replace traditional corporate structures with decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), allowing people from anywhere in the world to participate in the blockchain job market. DAOs provide a tool for communities to form around common values or missions, and even mint crypto tokens allowing them to profit financially from their activity.
Finally, artists and creators rejoice at the thought of web3, since non-fungible tokens (NFTs) may give them more control over profits, royalties, and intellectual property.
Let’s have a look at what web3 is and how blockchain technology could soon move us into the future.
What is web3?
Web3 is being touted as the future of the internet. The vision for this new, blockchain-based web includes cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and DAOs. But what is web3 exactly?
According to the Ethereum Foundation’s timeline of the internet, web3 will be (and is already becoming) a decentralized version of the internet we know and love today. If today’s crypto evangelists are correct, people will soon use decentralized applications on blockchain in ways similar to how we already use internet-based applications.
Instead of your favorite streaming platforms, for instance, we may use blockchain-based music apps like Audius that reward listeners with social tokens and make it possible to pay artists royalties through NFT smart contracts. (And considering only about 22,000 of Spotify’s 11 million creators make more than $50,000 annually from their contributions, a more empowering model is arguably well overdue.)
Web3 may also include other decentralized platforms for consumers to store and share information, enjoy memorable experiences, invest, or even play games on the web. For instance, Filecoin could offer a decentralized replacement for Google Drive. Sator could provide a watch-to-earn model letting us profit from watching our favorite movies. Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols like Beefy could help us act like our own banks and profit from lending and staking cryptocurrencies without the need for institutional intermediaries. And gamers could interact with friends while making money through trading card battles on Splinterlands.
These platforms already exist and are being used by thousands (in some cases millions) of crypto enthusiasts around the world. Some say it’s just a matter of time before web3 tools become more user-friendly and decentralization becomes more widely adopted.
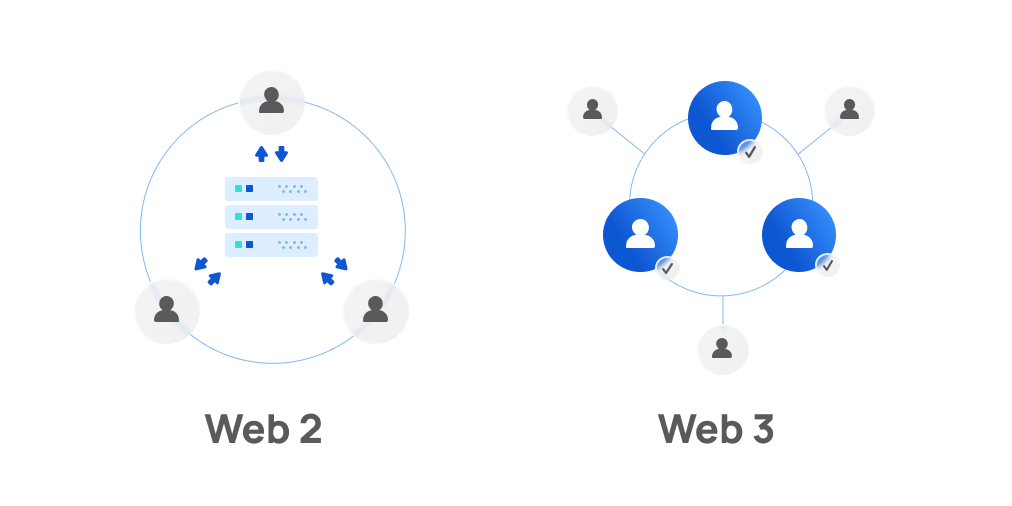
The difference between web2 and web3
The main difference between web2 and web3 is who controls the data. As it stands now, mega-corporations like Facebook, Google, Apple, and Amazon own user data in exchange for the “free” services they provide. We don’t say this to knock web2 companies entirely — even the Ethereum Foundation recognizes the centralized web has helped onboard billions of people to a vast, robust information-sharing network that has arguably improved people’s quality of life.
That said, just a handful of companies now have a stronghold on how we engage in commerce, communication, and data sharing. We have few alternatives if we were to opt out of the system, and consumers are never compensated enough for the ways our information is used for profit-generating activity by the entities to which our data is sold.
Not to mention, putting our internet usage in the hands of a few, select companies makes us much more susceptible to censorship. Web3 has the potential to be more censorship-resistant than web2.
Web3 technology
Blockchain is the foundation of web3. This technology is a new form of data storage and ledger-keeping. The name “blockchain” comes from the way information is digitally processed. Algorithms validate batches of information with a cryptographic process known as a hash. When this happens, the information batches get linked together in blocks that form a chain (hence the name). Blockchain is known for being tamper-proof because a person can’t invalidate one block without changing all of them, thus sending red flags through the whole system. And since blockchain runs through multiple computer networks known as nodes, it’s difficult to break into a truly decentralized chain and seize the data at once. These built-in security mechanisms are what allow blockchain to be a trustless ledger system in which all people can verify data.
Second-most important to web3 is something known as a smart contract. Smart contracts are algorithms that perform pre-coded functions when triggered according to certain rules. There are several types of smart-contract blockchains, with Ethereum being the original and most widely used. Through smart contracts, web3 users can have more autonomy over financial transactions. Some also speculate that smart contracts will renew public confidence in other important societal functions such as voting, real estate deeds, and more.
How does web3 work?
The Ethereum Foundation lays out a nice framework that summarizes the way that web3 will likely operate (if, that is, today’s crypto startups are successful).
It’s important to remember that we’re in the process of building web3, and our contributions will influence the future of blockchain technology in all capacities.
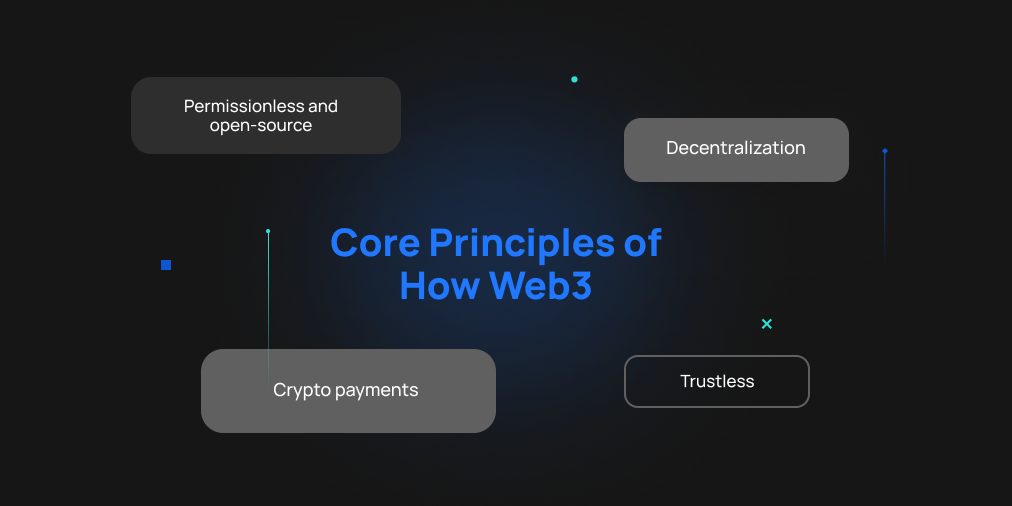
Here’s a summary of how the Ethereum Foundation describes the core principles of how web3 will work.
- Decentralization: Ownership will be distributed amongst builders and users, not concentrated into the databases of mega-corporate entities.
- Permissionless and open-source: Everyone in all geographic regions will have equal access to participate in commerce, data storage, social experiences, and information sharing — along with any future applications of web3 we haven’t considered yet too!
- Crypto payments: Participating in a web3 world will require the use of cryptocurrency. Crypto natives argue this is superior to relying on the outdated infrastructure of banks and payment processors to send money online.
- Trustless: Blockchain’s transparent ledger allows for every consumer and digital citizen to take action without putting their faith and trust into institutions. Much like a pick-up basketball game in which every player is equally invested, web3 will rely on economics and transparency to incentivize behavior and allow people to make informed choices.
Is web3 the future?
Knowledge about web3 is picking up steam. According to Google’s keyword planner tool, search volume for the phrases “web3” and “web3 crypto” has increased 900% since last year, averaging as many as 100,000 searches per month.
Of course, 100,000 people isn’t exactly mainstream. (As a comparison, the word “Beyonce” has as many as 10 million searches per month.) But despite the crypto industry’s volatility, institutional money is making its way into the most popular decentralized protocols behind the scenes. Many projects are in stealth mode, and developers typically see bear markets as opportunities to build with a lean, scrappy team.
That said, web3 currently has some serious limitations. Web3’s limitations include scalability issues (too many new people crowding the network), UX problems (the tools are built by tech-savvy developers and not super friendly to the average person), education (not enough people are familiar enough to take the leap), and cost (Ethereum’s gas fees are high, and crypto is too volatile for people afraid of losing money).
But despite the limitations, the long-term vision of web3 is already well underway. Web3 is nothing new to crypto natives and industry professionals who’ve been operating in the space for nearly a decade. Projects will rise and fall, yet blockchain’s applications continue to evolve beyond our own imaginations.

